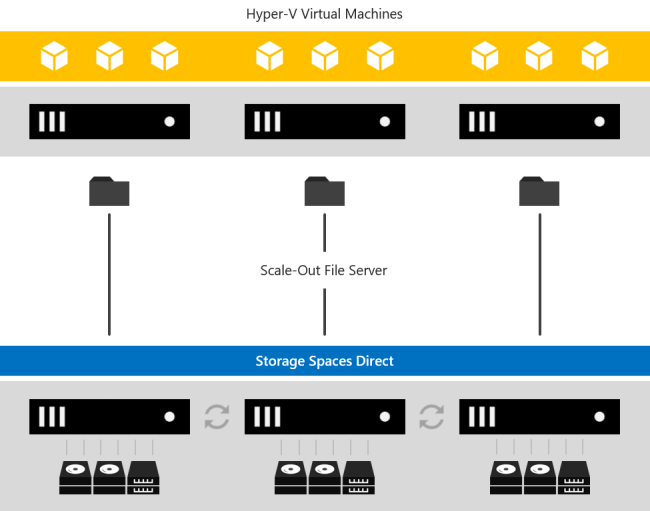
Microsoft S2D Hyper Converged Malaysia

Microsoft Hyper Converged Solution Provider Malaysia
One of the main benefits of the virtualization of an environment is rational resources usage. When specific virtual machines are not needed, they can be powered off; this allows freed up computing resources to be provisioned to the VMs that are needed. Hyper-V Failover Cluster allows you to reduce downtime in your virtual machines; and beginning from editions for Windows Server 2016, Hyper-V can provide VM load balancing between Hyper-V hosts (which are called cluster nodes in this case).
Load Balancing automatically checks a Hyper-V cluster state, and then depending on the results and settings found, it initiates VM migration from the overloaded node to the less loaded node in order to redistribute loads across Hyper-V hosts.
There two methods that can be used to check host loads:
- Checking RAM (random-access memory) utilization. Insufficient memory on a Hyper-V host is one of the most common problems, and can cause lags.
- Checking CPU (central processor unit) utilization. Insufficient processor capacity can also cause lags.
The more CPU and RAM resources are consumed by a host, the more loaded the host is considered by Hyper-V. If periodic load balancing is configured for a cluster, then the load of the hosts is evaluated every 30 minutes. You can also evaluate the hosts’ load on demand. A system identifies the hosts in which the load exceeds the defined threshold, as well as the hosts in which the load is under the threshold value. If the current load of cluster nodes is uneven and meets the mentioned conditions, Hyper-V will initiate VM live migration between the nodes. Hyper-V Live Migration allows you to perform VM migration unnoticeably, and without significant downtime.
The integration of Load Balancing with a Hyper-V Failover Cluster is provided. The following clustering rules are honored for load balancing: Possible Owners, Anti-affinity (these two rules existed before Windows Server 2016), and Fault Domains (new).
The Possible Owners rule defines the Hyper-V hosts for which the migration can be performed. This rule only defines possible VM owners, and can prevent VM migration to unwanted hosts.
Anti-affinity rules allow you to prevent running two defined VMs on the same host. For example, if you have two VMs with both a primary and a secondary Domain Controller that must not run on the same host. This approach increases reliability in a case of the host with one of the Domain Controllers fails.
Fault domain is a feature that defines a set of Hyper-V hosts that can be affected for some types of physical failure, for example, network failure, power failure etc. Hyper-V hosts with VMs of the same fault domain are usually connected to the same power source and network switch, thus they can be mounted to the same rack. If any failures occur, then all VMs of the same fault domain would be affected. A cluster can be logically broken (divided) into multiple fault domains, and failure of one domain should not affect other domains.
Configuration Parameters
Load Balancing is enabled by default for Failover Clusters in Hyper-V 2016. There are two types of behavior: “Use only when a new node is added to the cluster” and “Check with time intervals”.
Use only when a new node is added to the cluster. In this case, a cluster gets more CPU as well as RAM resources, and extends the overall computing capacity. A system evaluates the load of each node. If any of the nodes are overloaded (a threshold value set in the configuration is exceeded), then the appropriate VMs are migrated from overloaded nodes to recently added nodes that have free resources. This option is useful if you regularly add capacity to your Hyper-V Failover Cluster, and may be useful for clusters based on Storage Spaces technology. This option doesn’t have an impact on a cluster if the node that was previously disconnected from the cluster (for maintenance, for example) is connected back to the cluster.
What Service Do Swisspac Provide for Microsoft Hyper Converged Solution?
DESIGN > DEPLOY > SUPPORT > MAINTAIN > EXTEND